Mars exploration is the concern of the Earth people, and the mysterious Mars may be unveiled step by step in the near future.

Mars is essentially a desert planet, with dunes and gravel all over the surface and no stable liquid water. (On September 28, 2015, NASA announced that there was a small amount of water on Mars. According to Agence France-Presse on July 25, 2018, researchers from the European Space Agency (ESA) said that the first liquid groundwater lake had been discovered on Mars. The atmosphere dominated by carbon dioxide is thin and cold. Sand and dust are suspended in it. Dust storms often occur every year. The polar cap of water ice and dry ice at both poles of Mars will rise and fall with the seasons.

Compared with the Earth, Mars is less active in geology, and most of its surface topography was formed during the more active period in ancient times. There are dense craters, volcanoes and canyons, including the highest mountain in the solar system: Olympus and the largest canyon: Sailor Canyon. Another topographic feature is the distinct difference between the northern and southern hemispheres: the southern part is an ancient crater-filled plateau, while the northern part is a younger plain.
Mars has two natural satellites: Phobos and Phobos, irregular in shape and possibly isolated dwarf asteroids. On Earth, Mars is visible to the naked eye, with a maximum brightness of - 2.9 and so on. Among the eight planets, Mars is darker than Jupiter and Venus. On September 28, 2015, NASA announced the presence of mobile water on Mars.
On July 25, 2018, AFP reported that the first liquid water was found on Mars.
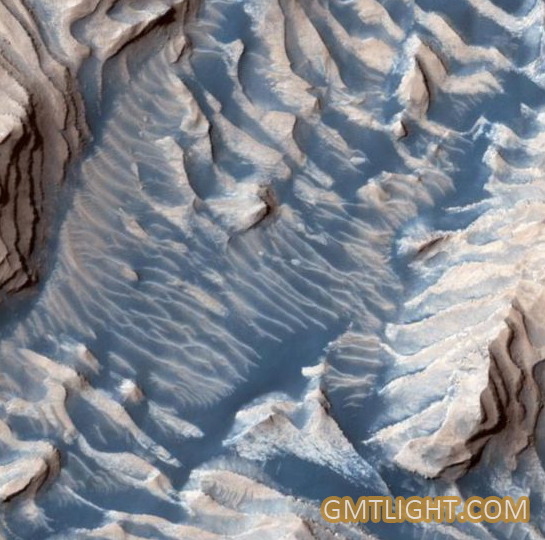
On September 21, 2019, NASA released a photograph taken by the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter spacecraft on September 19. NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter took a picture from Danielson Crater, 42 miles southwest of Mars. Pictures show that rocks and sand are frozen together in the crater. Over the years, the number of sediments in meteorite mouths has been changing, with some areas resisting erosion and others being erased. Blue sand on the stepped prominence of Mars. NASA says this will almost lead to a stepped bulge. The sand here is blue and scattered on the ridge.
"Migrating to Mars is a human dream, which may come true. However, the current move to Mars is costly and time-consuming, requiring cheaper spacecraft and more convenient energy. Mr. Niu, gmtlight.